THE DYSHIDROTIC ECZEMA. APPEARANCE AND TREATMENT
The dyshidrotic eczema, also known as dyshidrosis or pompholyx, is a recidivative eczema of chronic aspect which appears like a kind of vesicles of different sizes in hands and feet. The dyshidrotic eczema is not a contagious pathology and it appears making groups of vesicles with transparent or serohematic contents. Its cause is still unknown, although it has some relation with an immune alteration of the skin and the outbreaks of dyshidrotic eczema appear mainly when somebody is under stress or nervous tension. The dyshidrotic eczema appears more probably in those patients who have multiple allergies, sensitive skin or atopic eczema.
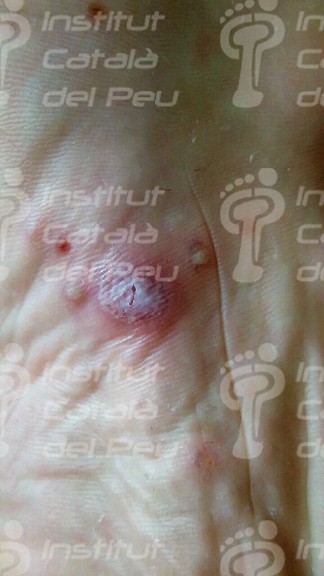
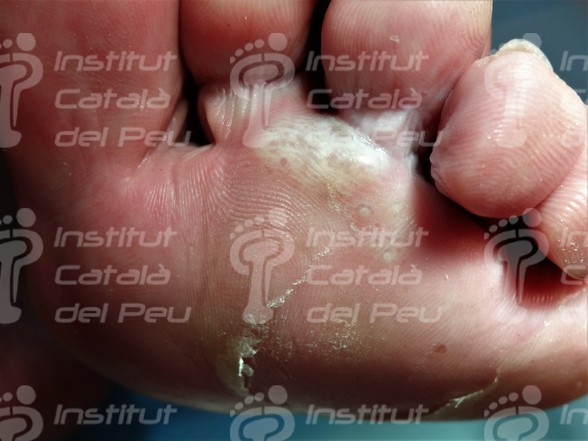
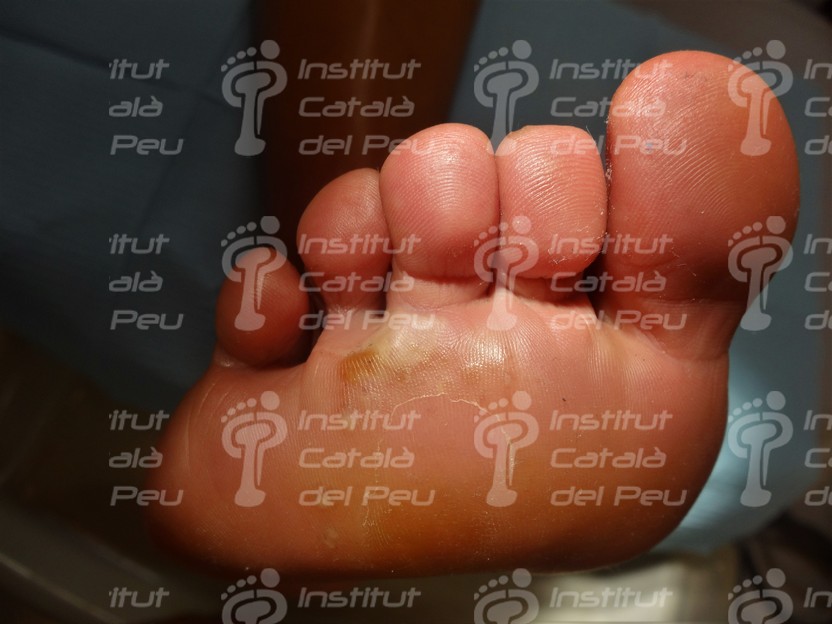
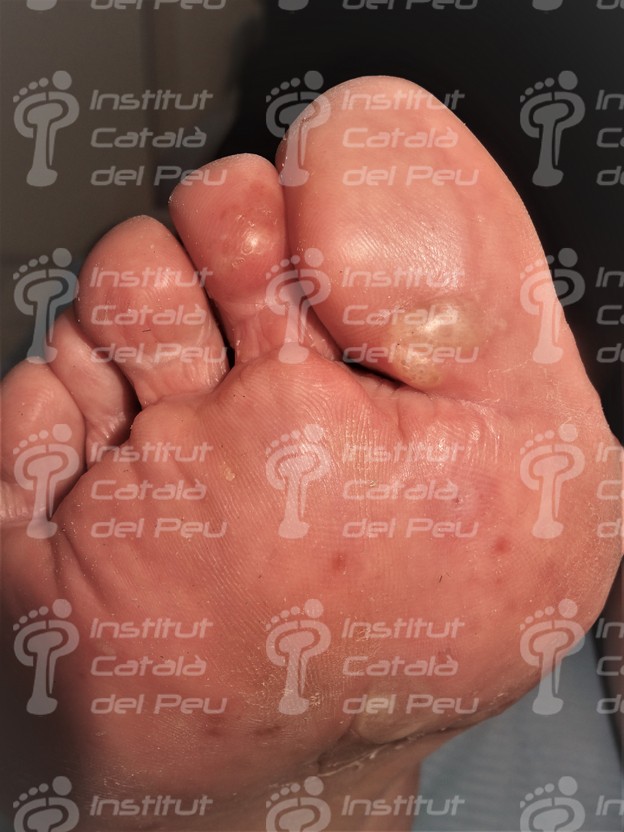
The dyshidrotic eczema makes small vesicles in the lateral sides of toes and soles of foot with a sensation of pain, itching and stinging. Once the vesicles have disappeared, the affected skin flakes until it completely regenerates.
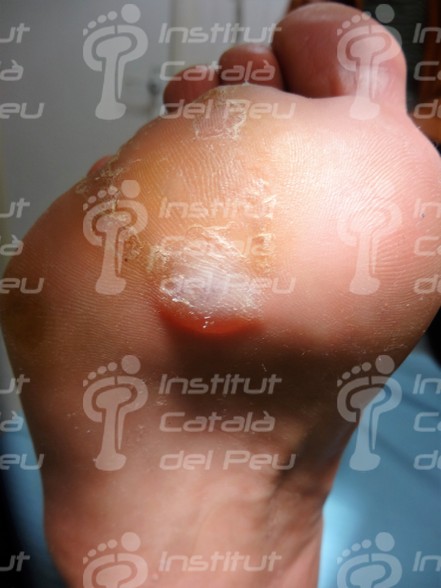
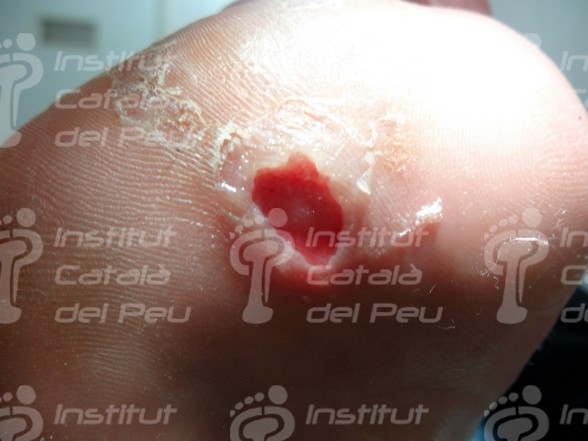
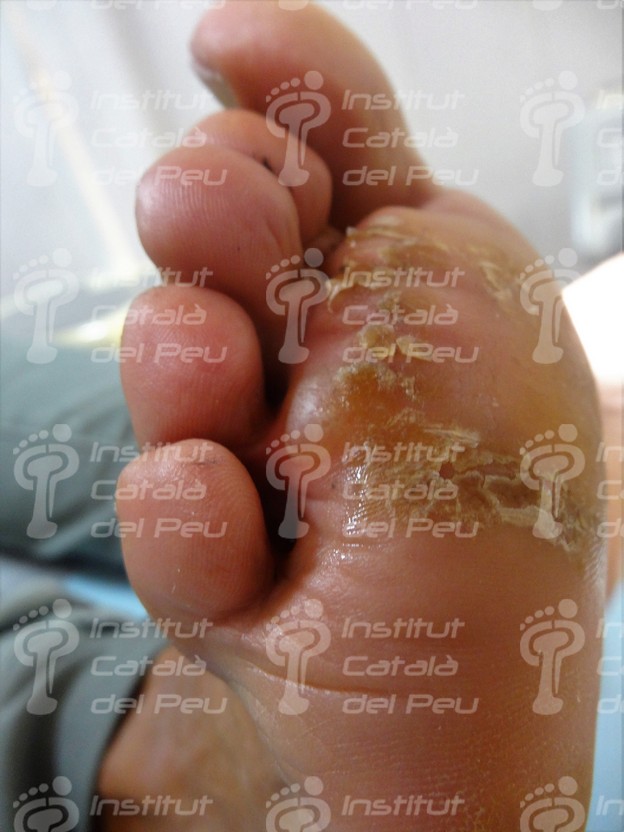
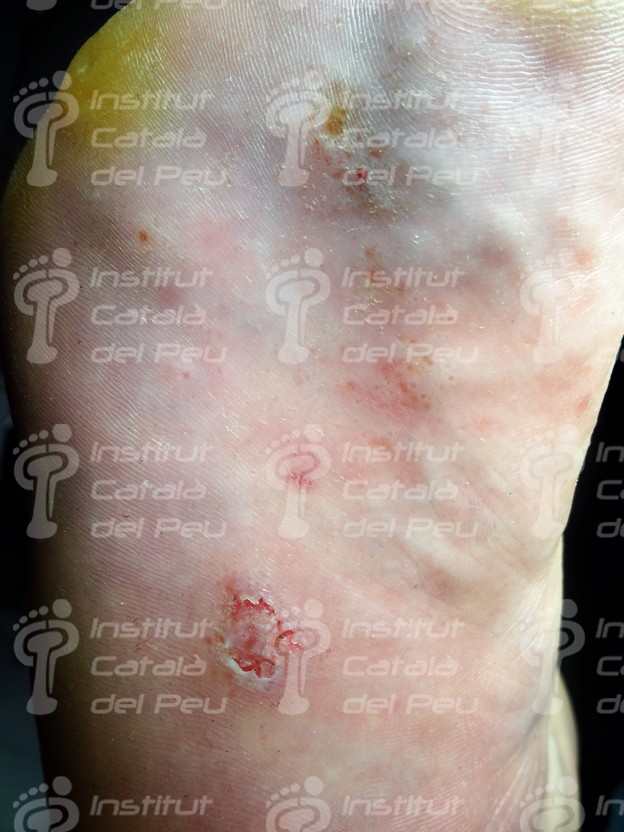
In case the dyshidrotic eczema appears with vesicles of slight or moderate intensity, they can cause desquamation of skin and, if vesicles are big, they can evolve to erosions and fissures. There are patients who have a vesicular appearance, while others have a more desquamative appearance when fissures appear.
In case the dyshidrotic eczema becomes infected by bacteria, the symptoms may complicate through the development of erythematous vesicles and pustules. In case of scratching the injured zone, it can appear a risk of infection.
It may appear skin thickness when vesicles have a recurrence in an erosive way.
The vesicles from dyshidrotic eczema approximately disappear in two or three weeks, being the healing quicker through the appropriate pharmacological treatment. For external use only, the biggest ampules must be drained and we can apply antibiotic cream. Wet or cold compresses relieve the symptoms.
When the dyshidrotic eczema appears you can choose different treatments and are the following ones:
- The application of potassium permanganate.
- Steroids cream for external use only with the aim of improving the desquamation and eliminating the irritation.
- Zinc oxide balsam.
- Moisturizing the skin in order to mitigate the dryness of the skin or possible fissures.
- Antihistaminics, depending on the itching level.
In more serious cases, the pharmacological treatments can be more aggressive, through the application of cyclosporine, retinoids and methotrexate.









Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!