Unguinal surgery minimally invasive
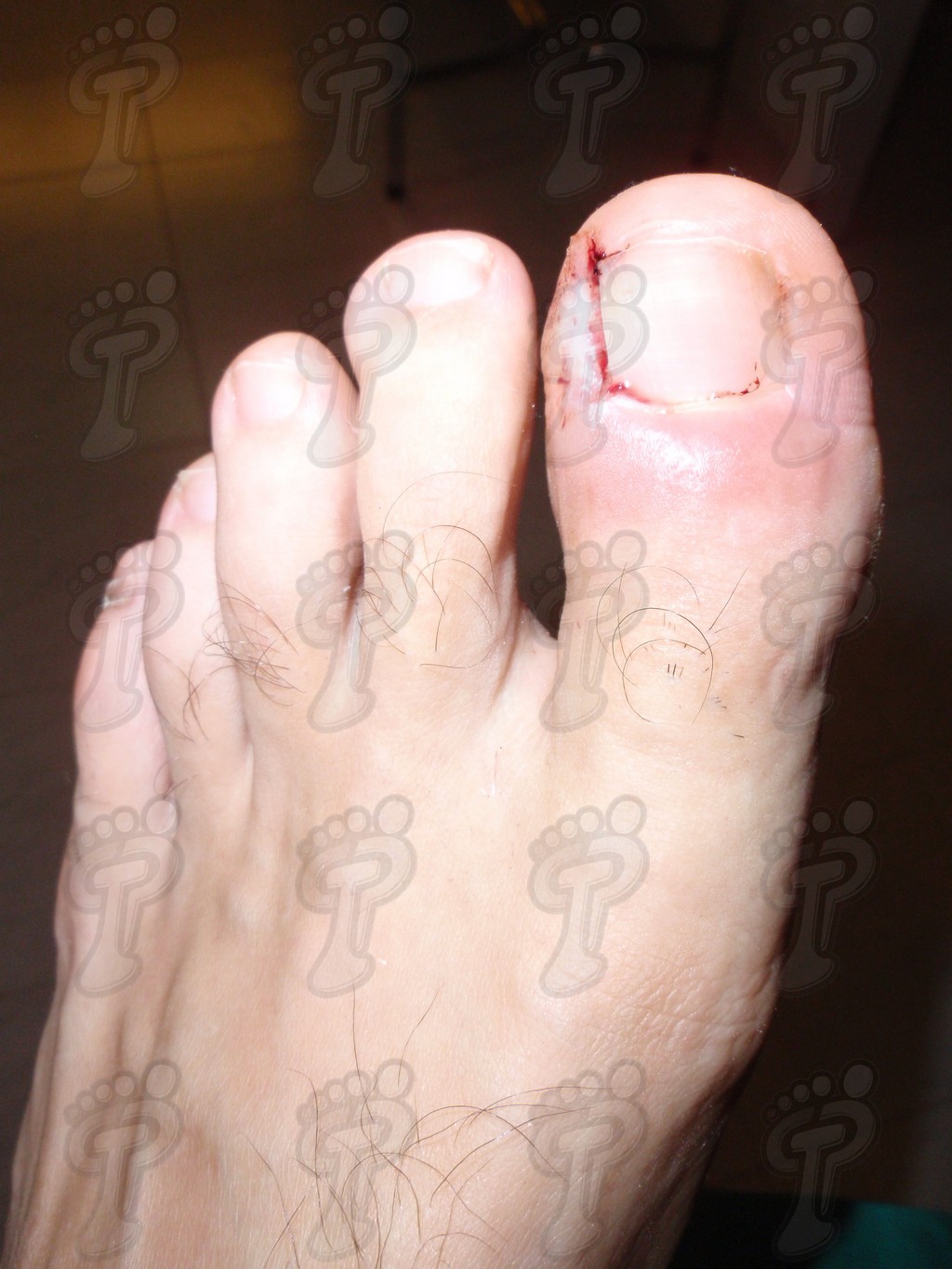
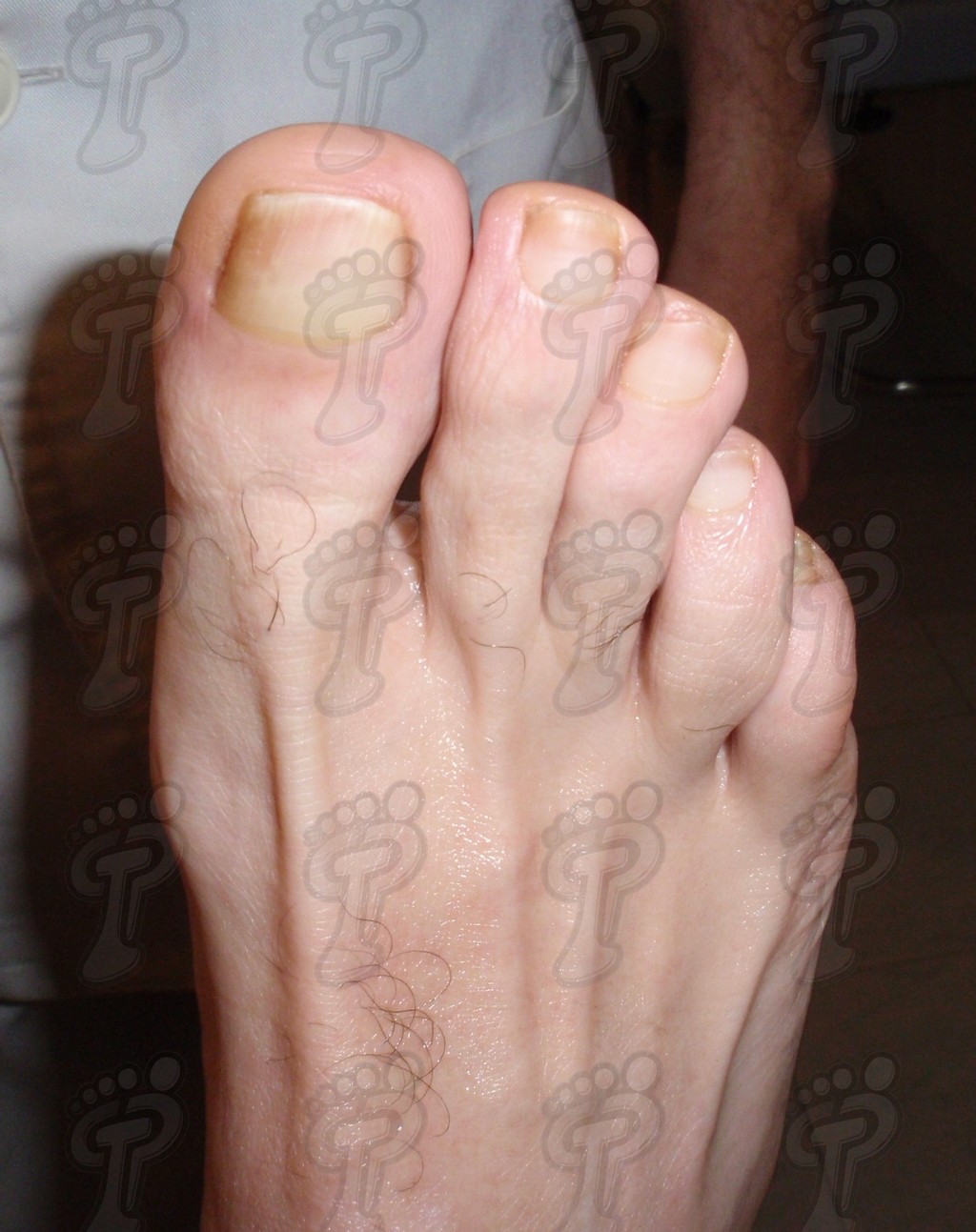
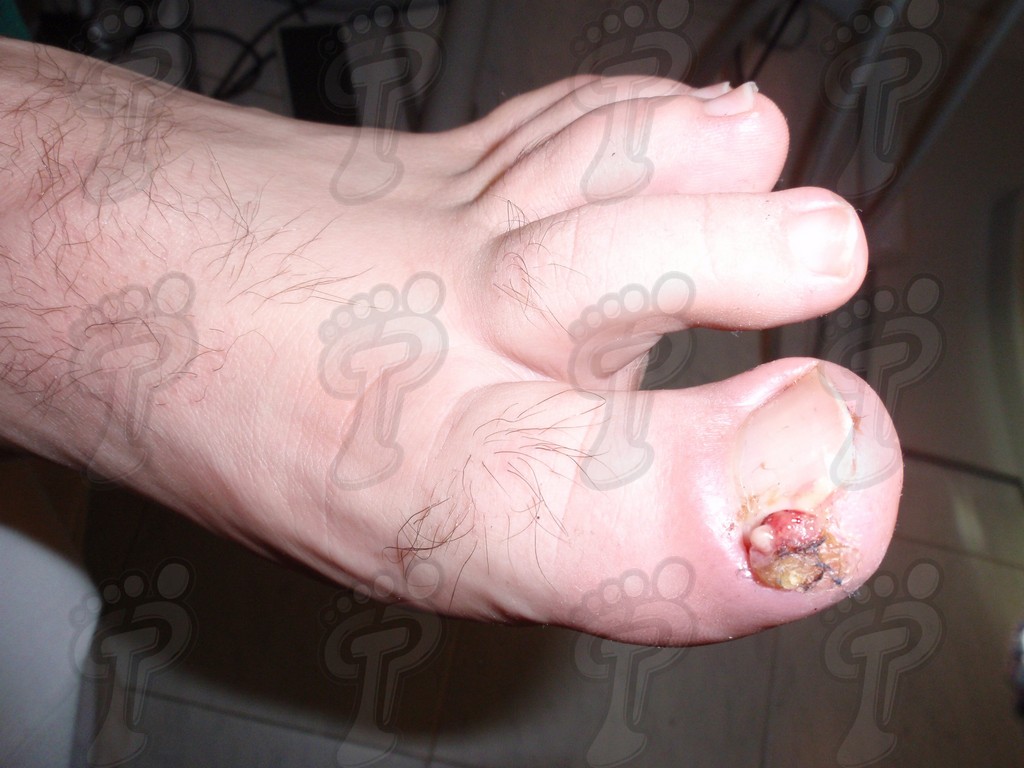
 The unguinal pathology produces a lot of surgical operations confronted to other surgeries which affects to the foot. There are countless techniques described which depend of the toe state, and of every professional’s skill and experience. The surgical variability takes in from the complete extirpation of the nail, the only resection from tender parts and in most cases, the production of the unguinal amplitude with different treatments. In this issue, I will show you a pair of techniques which I like to use most, provided they are suitable to the idiosyncrasy of the case. The choice of these techniques is due to its low indication of postoperative period pain and its quick recovery (approximately in 10 days). This method allows the patient to return to work and his social life in a short time.
The unguinal pathology produces a lot of surgical operations confronted to other surgeries which affects to the foot. There are countless techniques described which depend of the toe state, and of every professional’s skill and experience. The surgical variability takes in from the complete extirpation of the nail, the only resection from tender parts and in most cases, the production of the unguinal amplitude with different treatments. In this issue, I will show you a pair of techniques which I like to use most, provided they are suitable to the idiosyncrasy of the case. The choice of these techniques is due to its low indication of postoperative period pain and its quick recovery (approximately in 10 days). This method allows the patient to return to work and his social life in a short time.
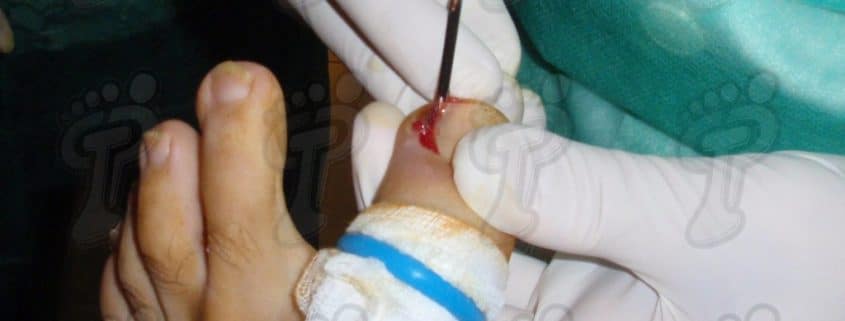
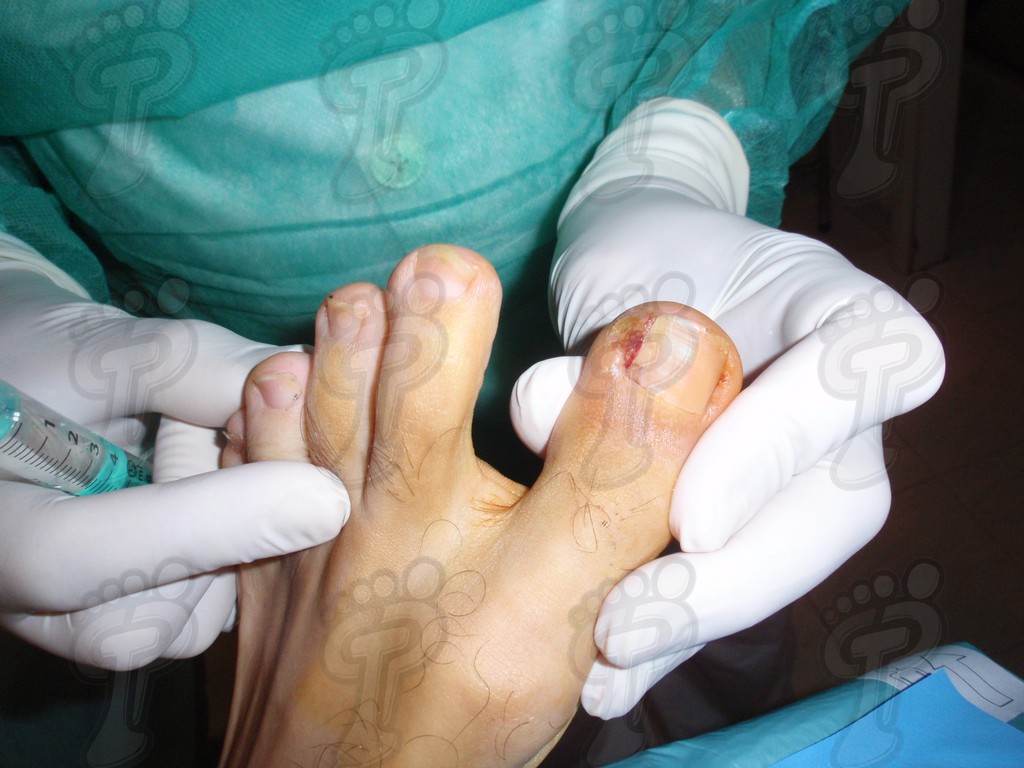
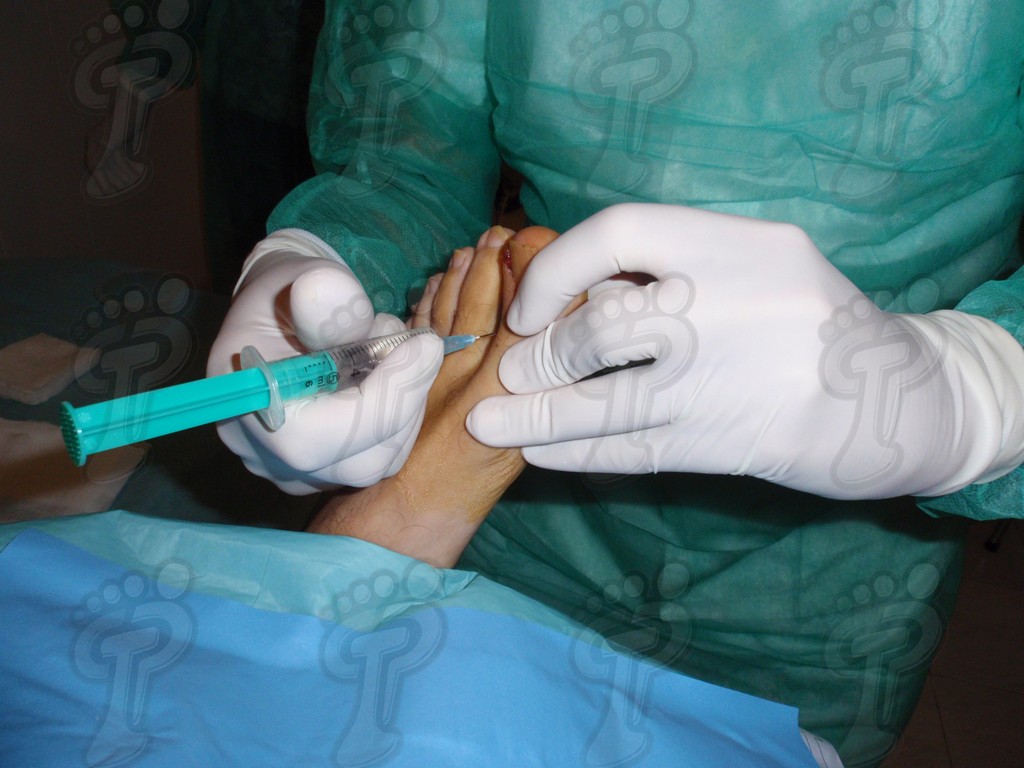
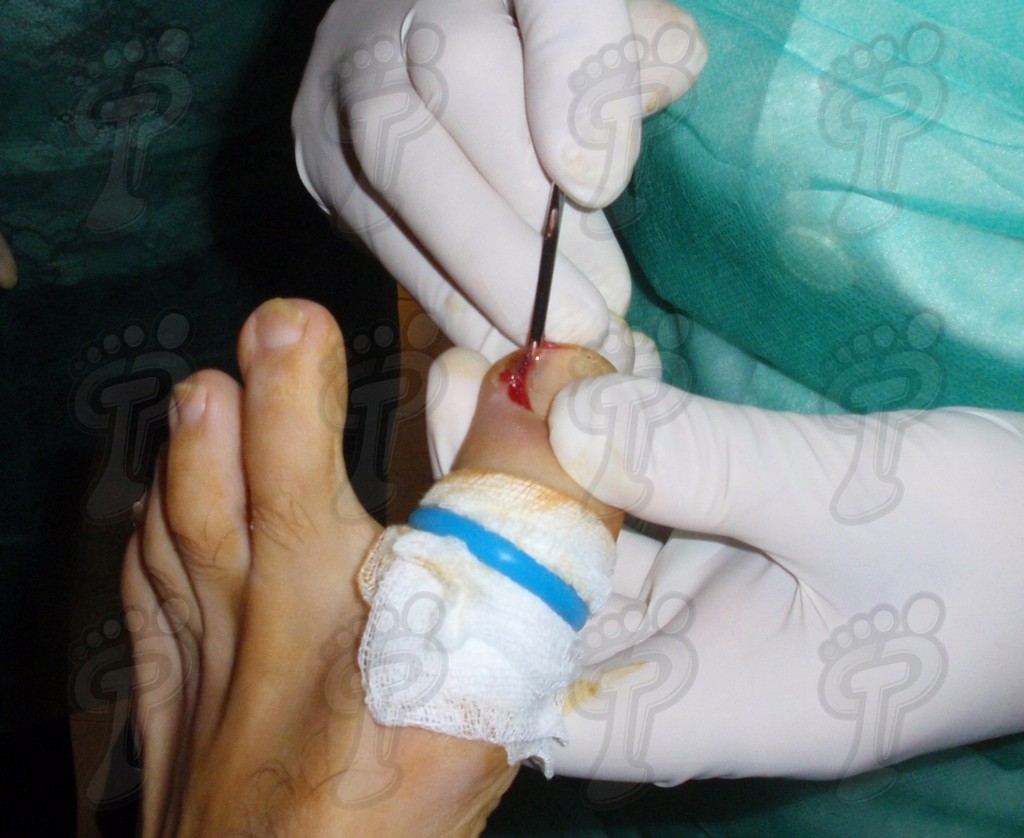
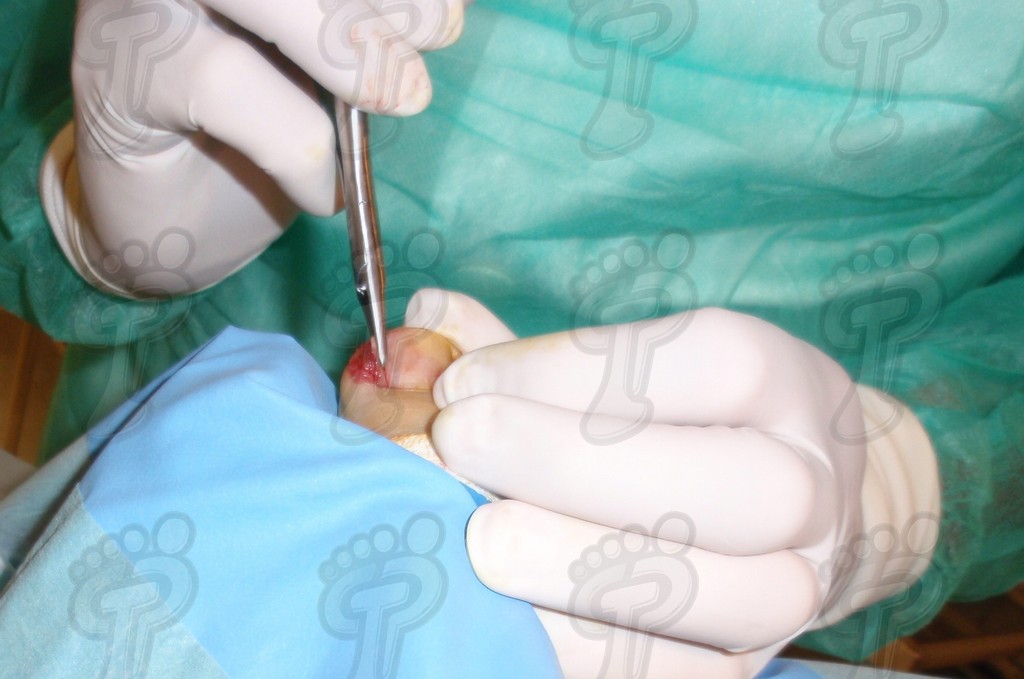
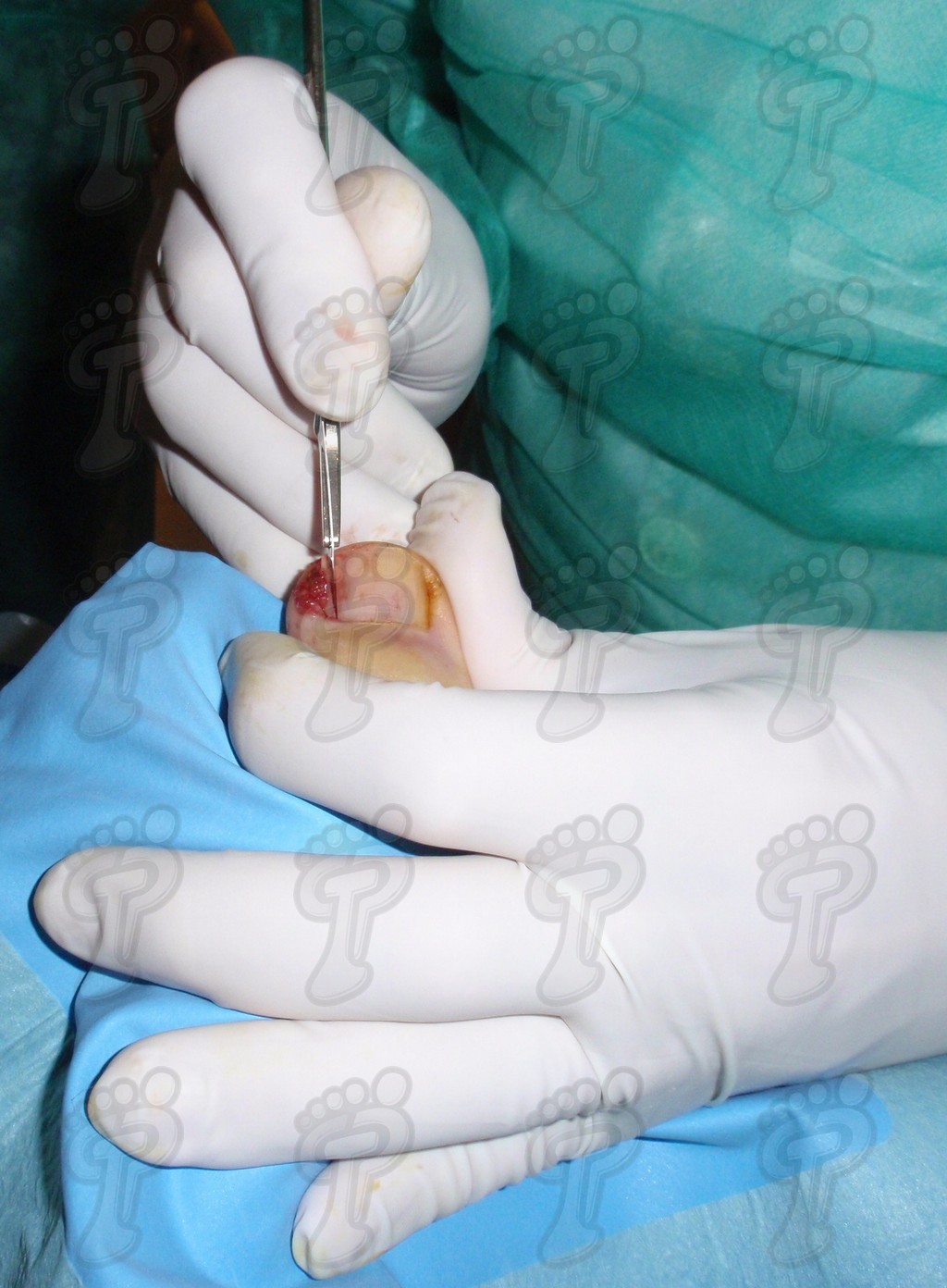
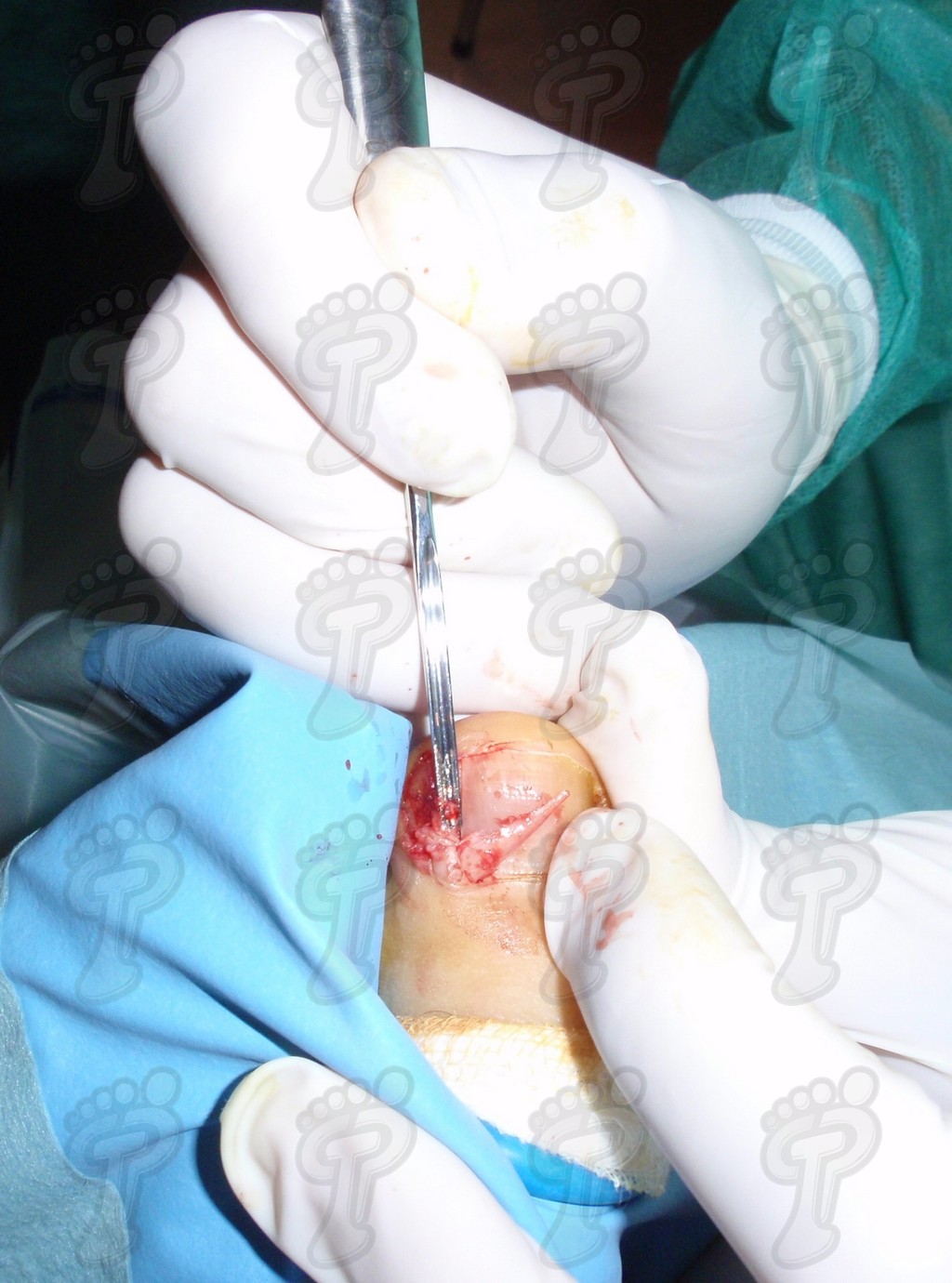
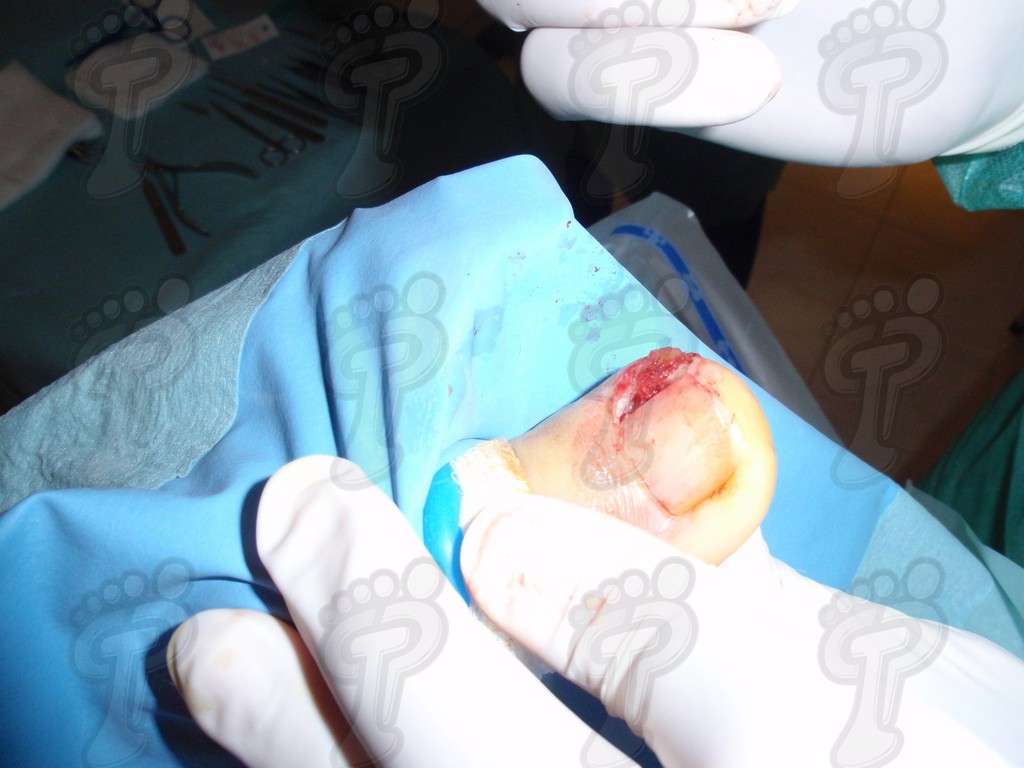
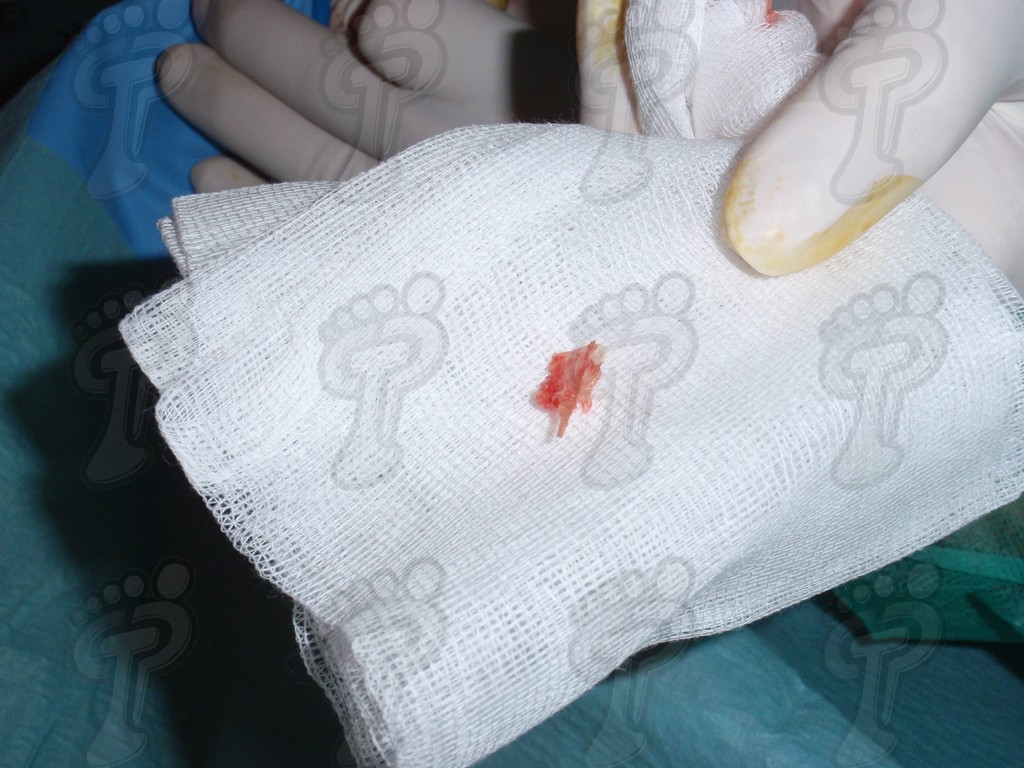
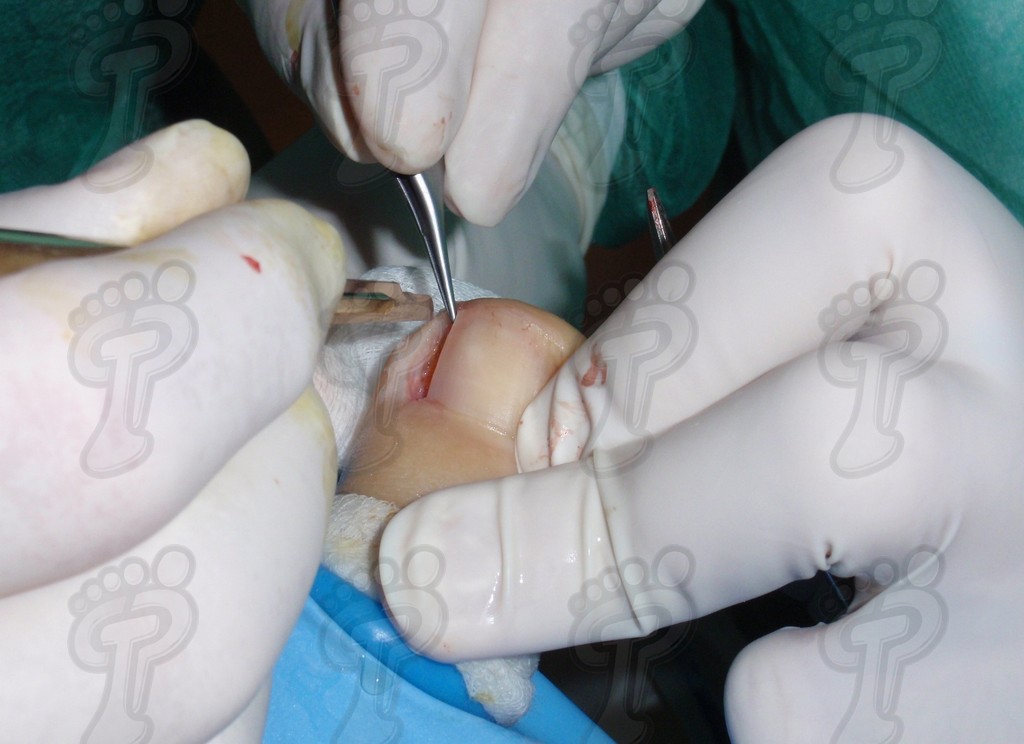
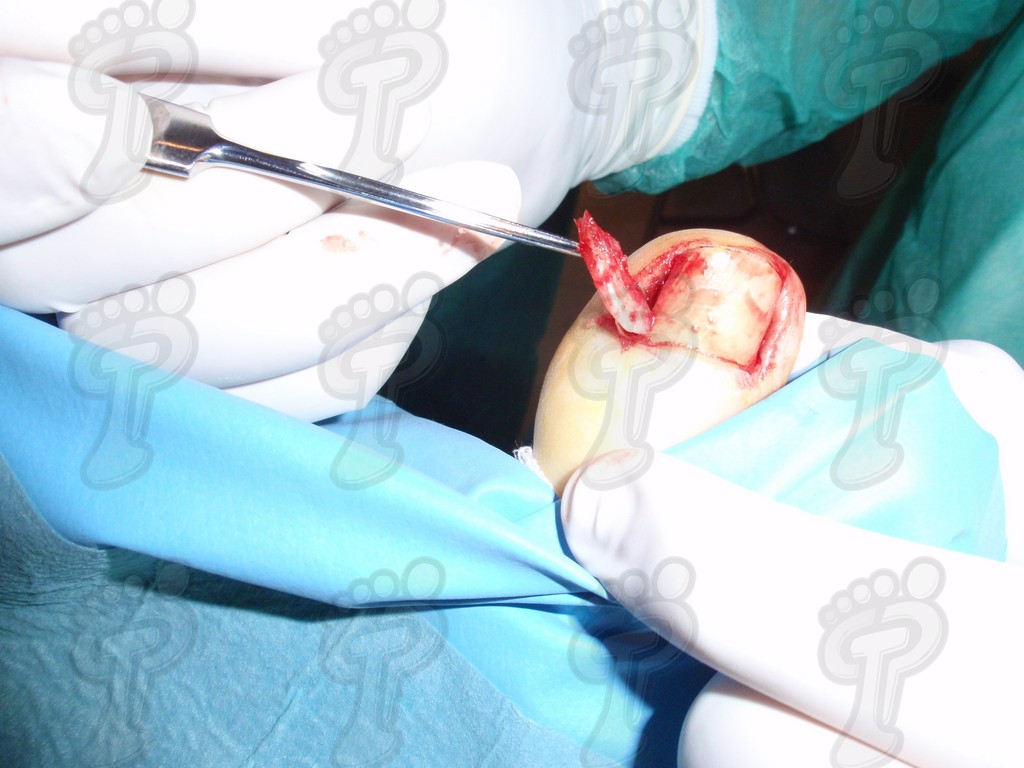
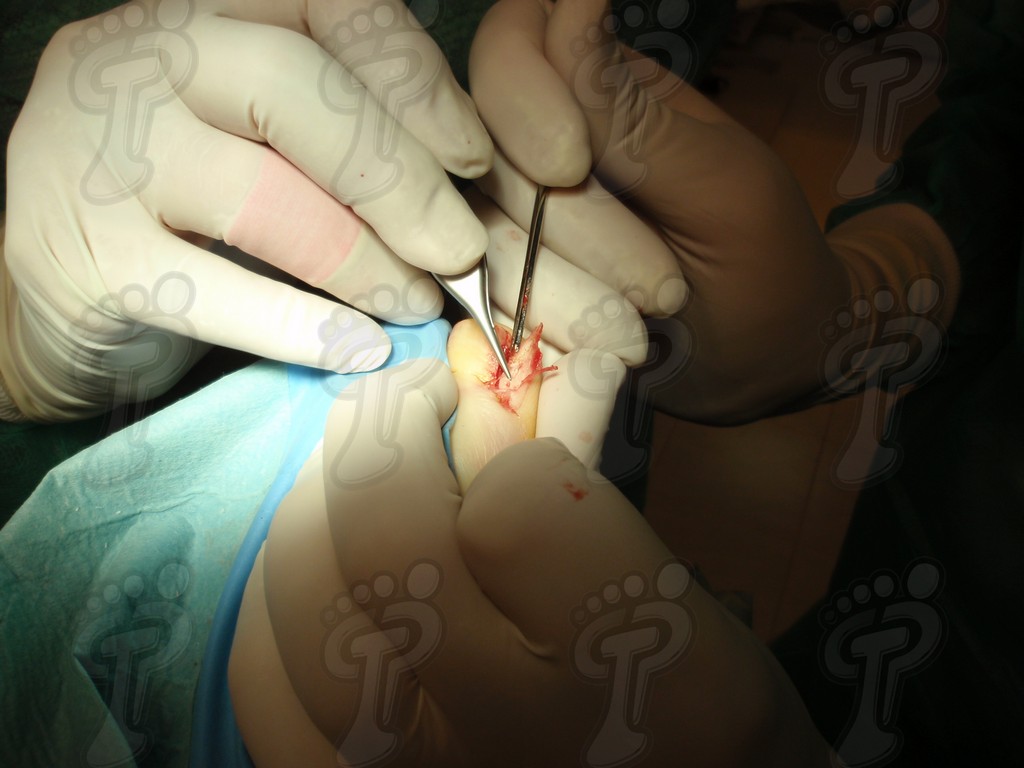
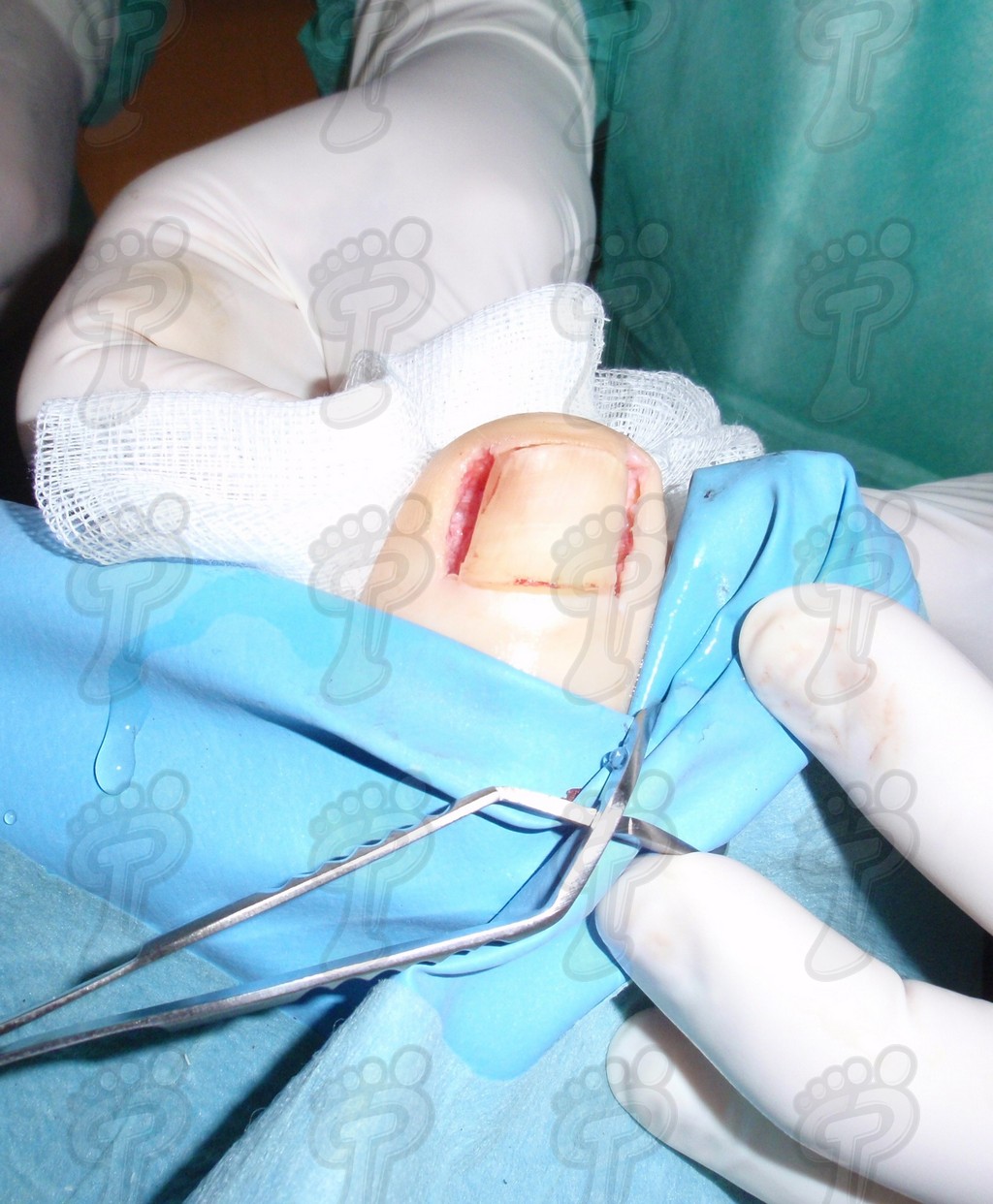
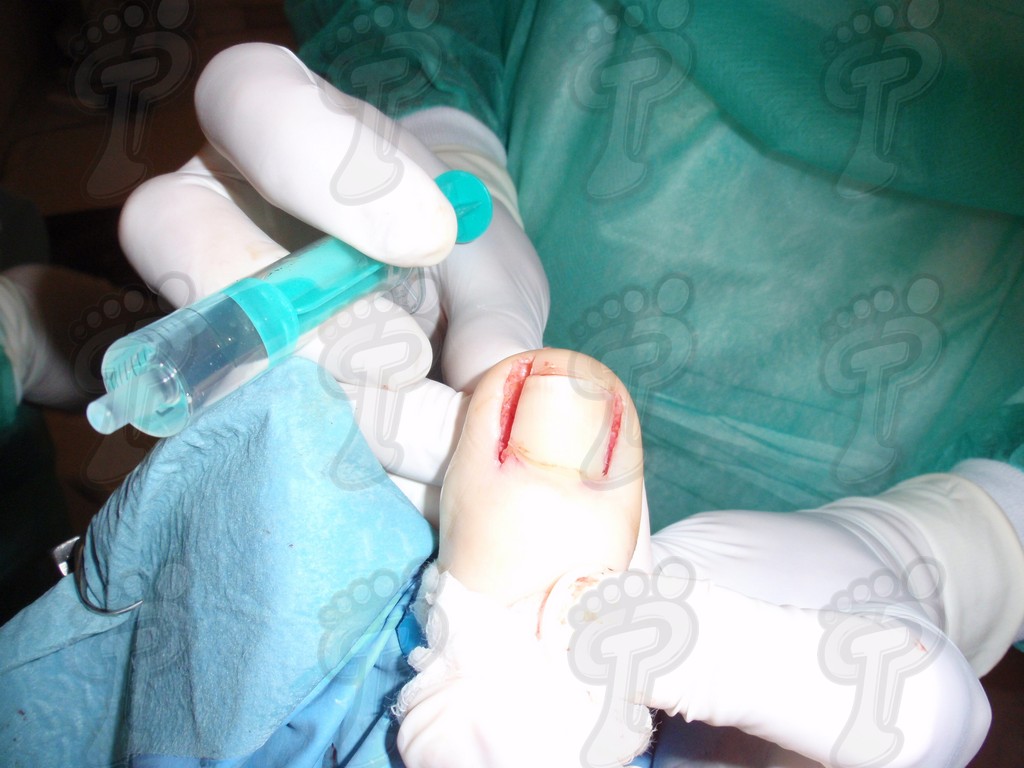
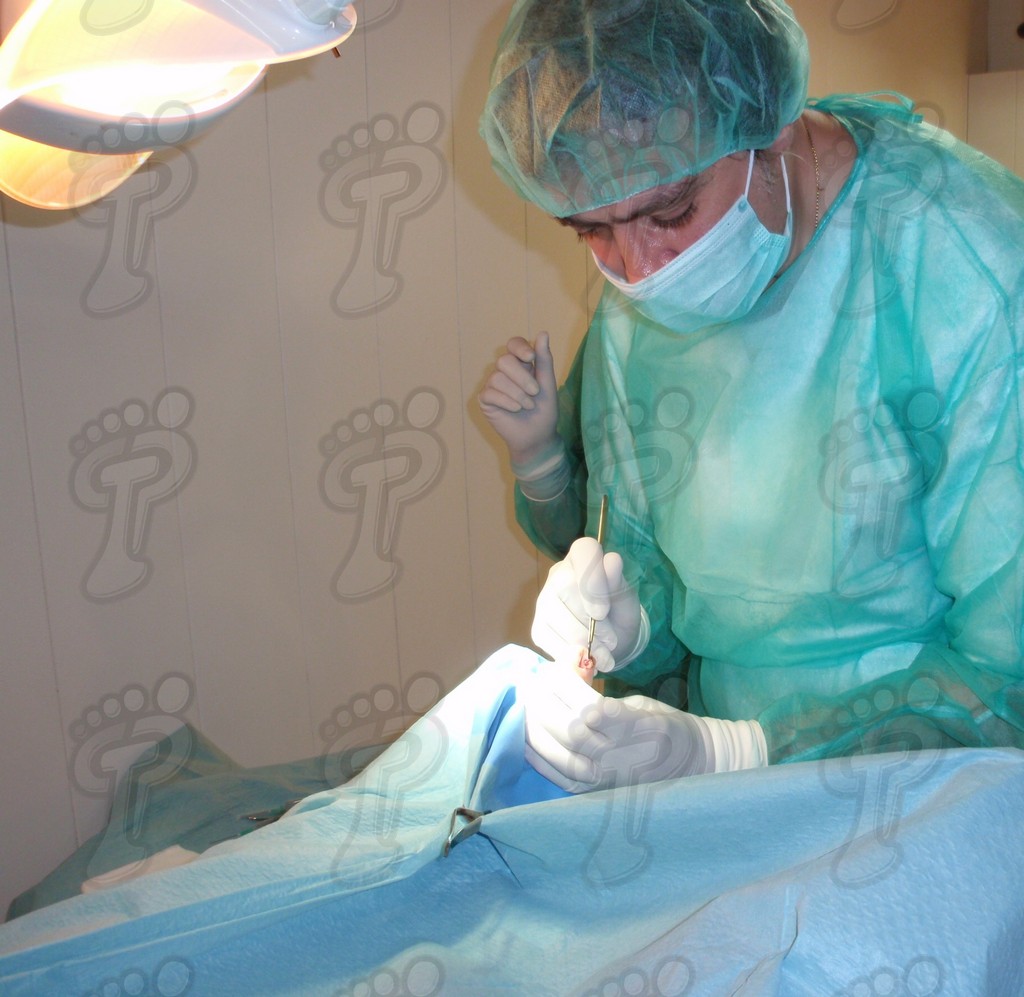
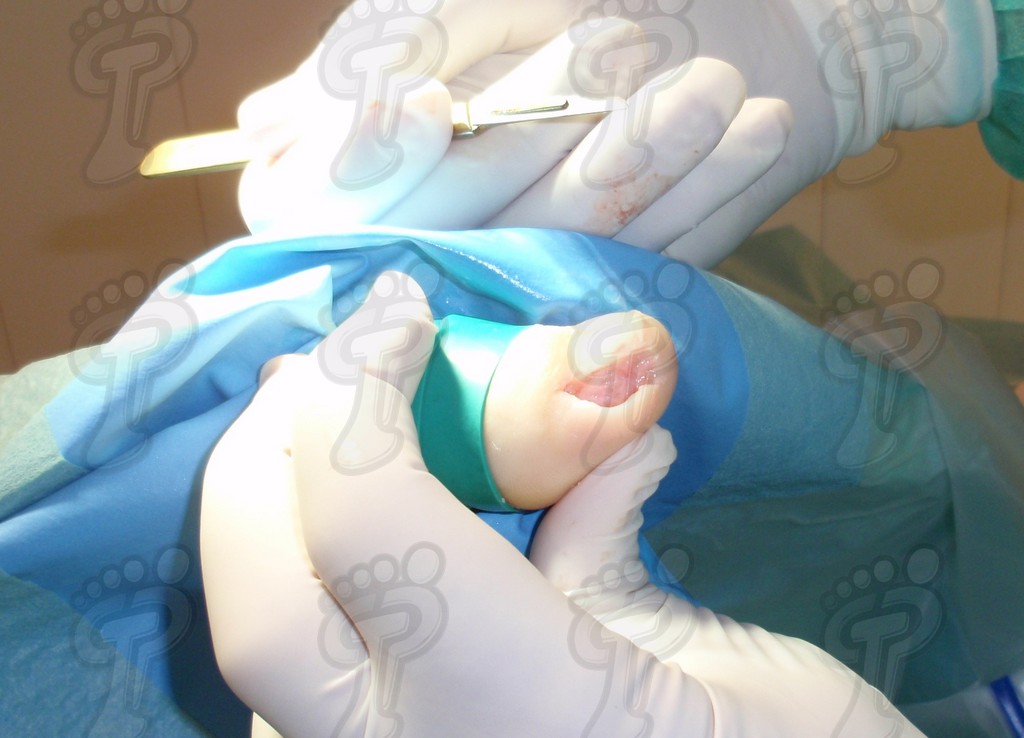
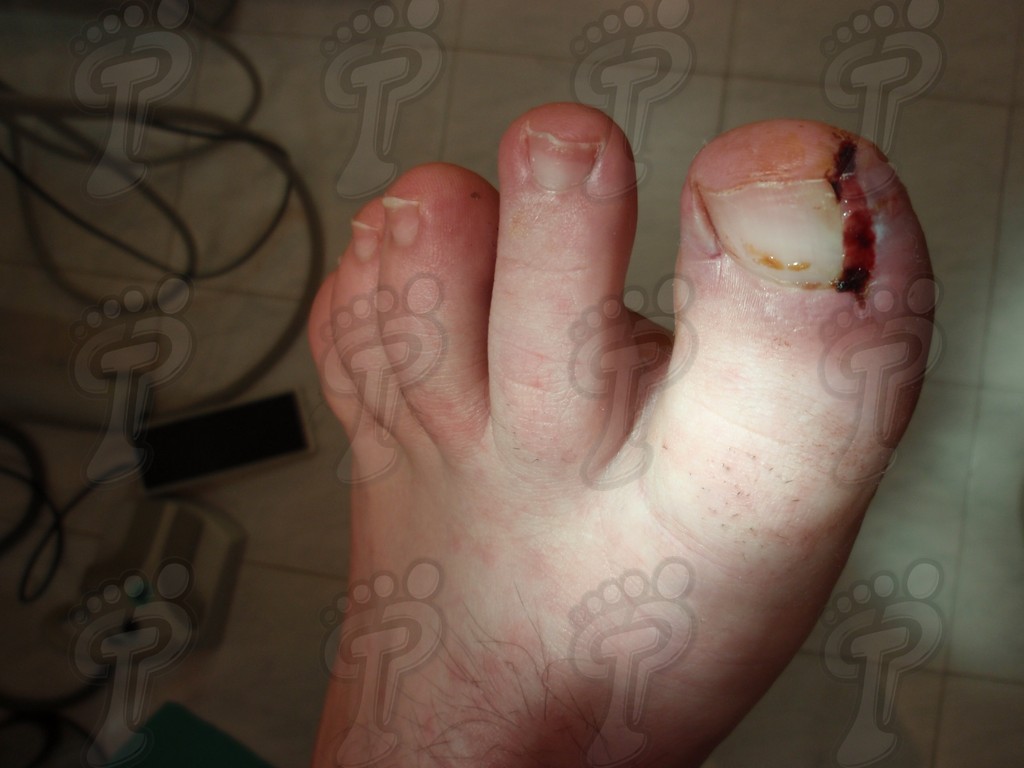
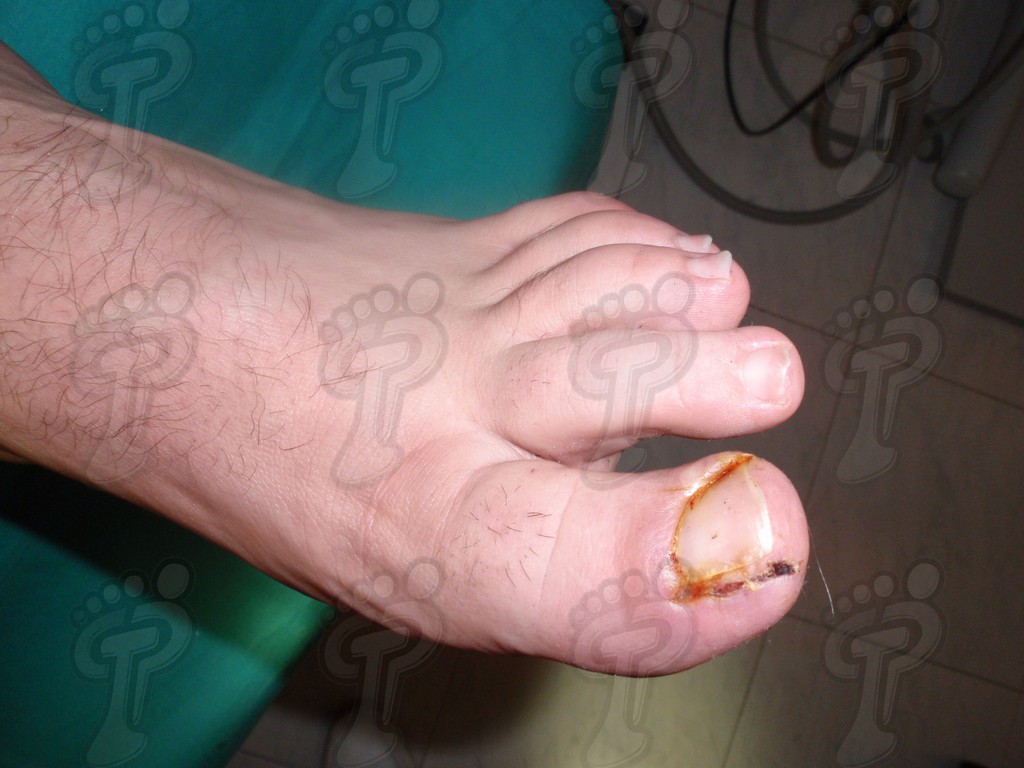
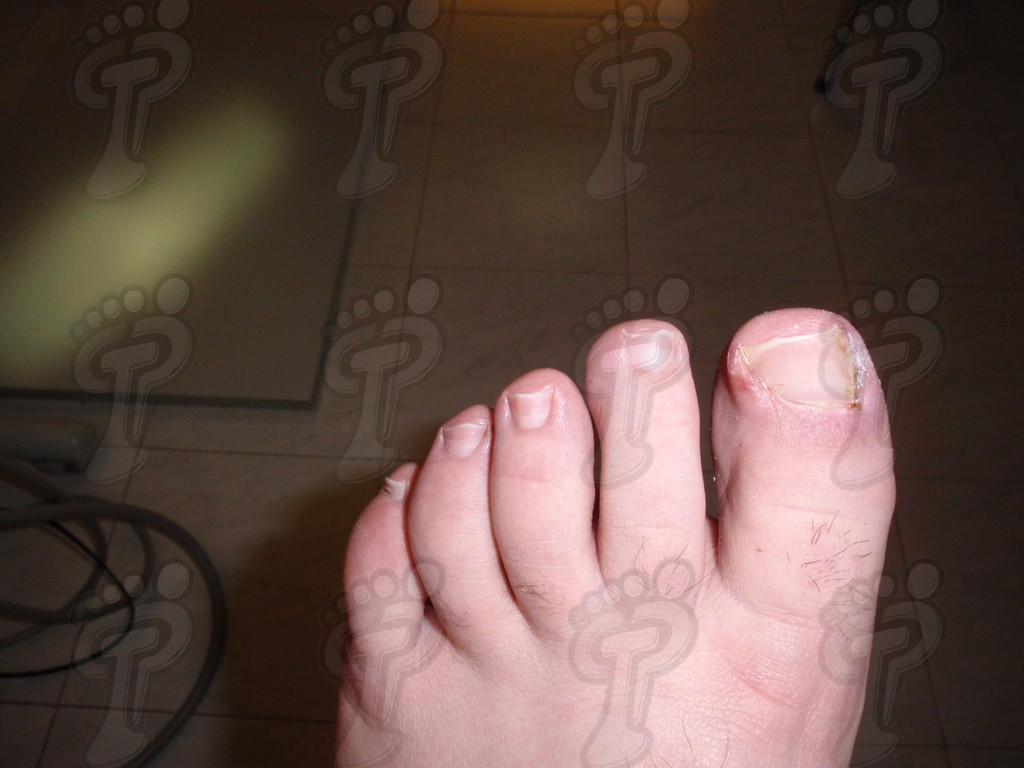
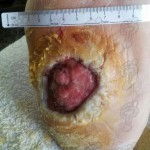
We operate on the unguinal lamina from the adjacent tissues by a precise gouge or chisel, with a previous anesthesia and preparation of the surgical materials. We have to separate the periungual parts, the Matrix unguis and the eponychium basically. In this way, we can limit the depth in which the Nail bed is located (key step for the D. and C. dilation and curettage process). We do the first cut by a metal shears giving an orientation to the matrix and respecting an 80% of the nail approximately. We use the gouge to withdraw the spicule and we curette the matrix in order to avoid recidivations by a small Martini spoon. We have to curette in all directions but towards the direction to the unguinal lamina which has to be respected, avoiding alterations in this case. If there exists an hypertrophiated tissue or devitalized by old inflammatory and infectious processes, we have to proceed to its exeresis by a bistoury. This surgical cleaning doesn’t stop to be a plastic regeneration with the aim of a correct esthetics of the toe and taking away the possibilities from a recidivation. The regeneration technique has as a main objective the perfect approximation of the surgical brims without tension, by a deep cut parallel to the unguinal lamina, from the eponychium to the most distal point of the nail and another parabolic cut, in the same direction as the previous one, taking in the whole tissue to extract.
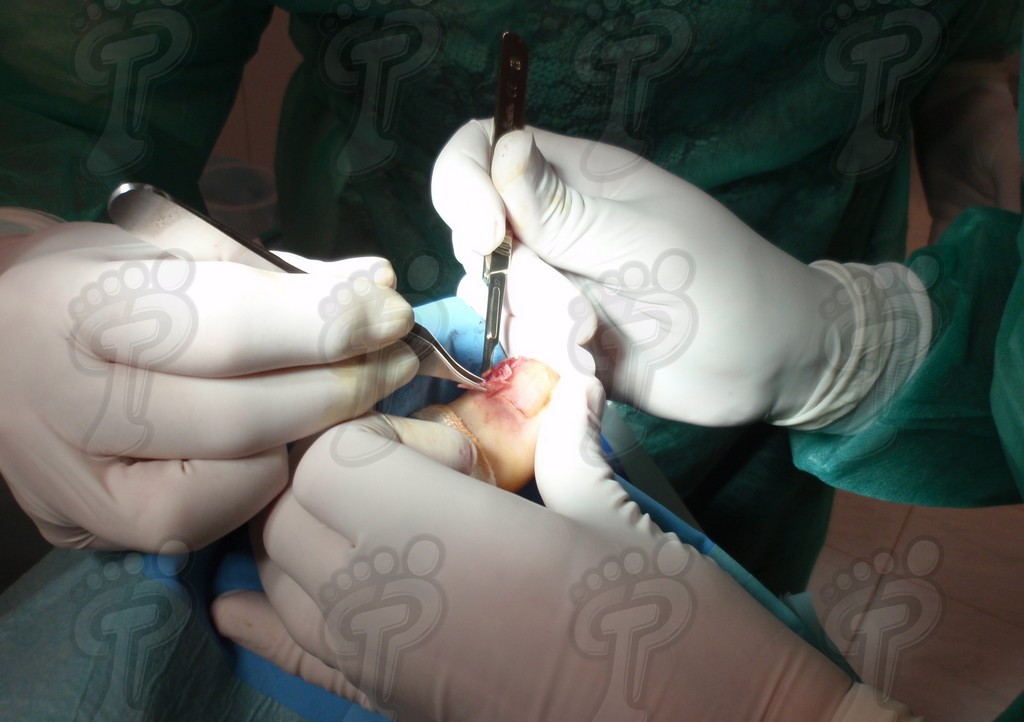
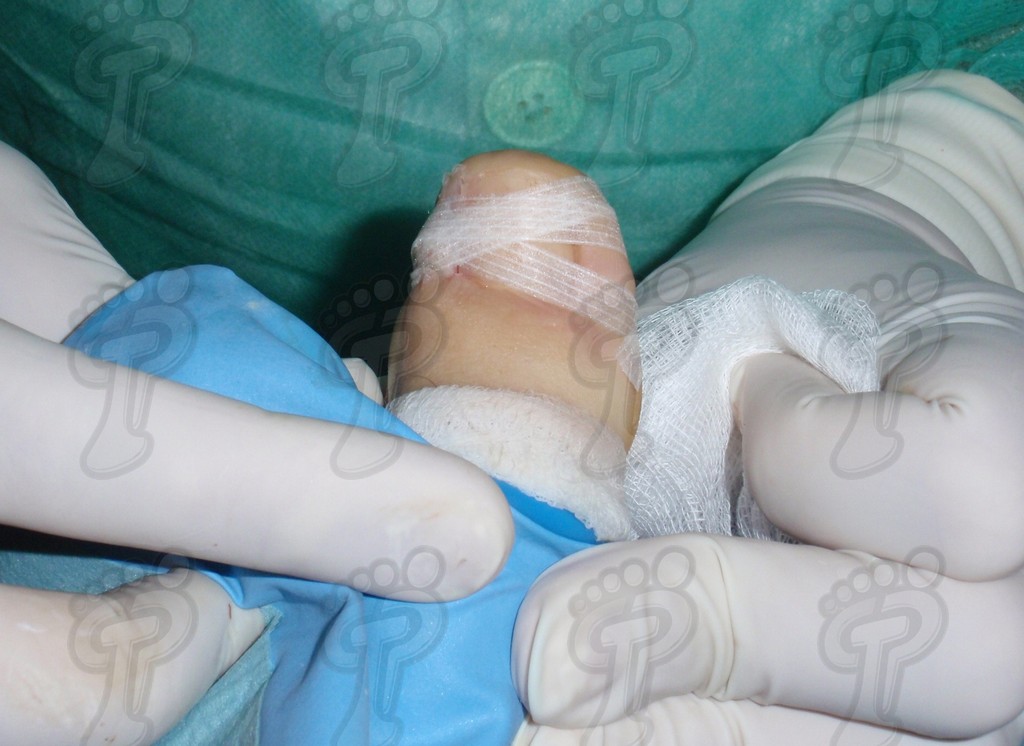
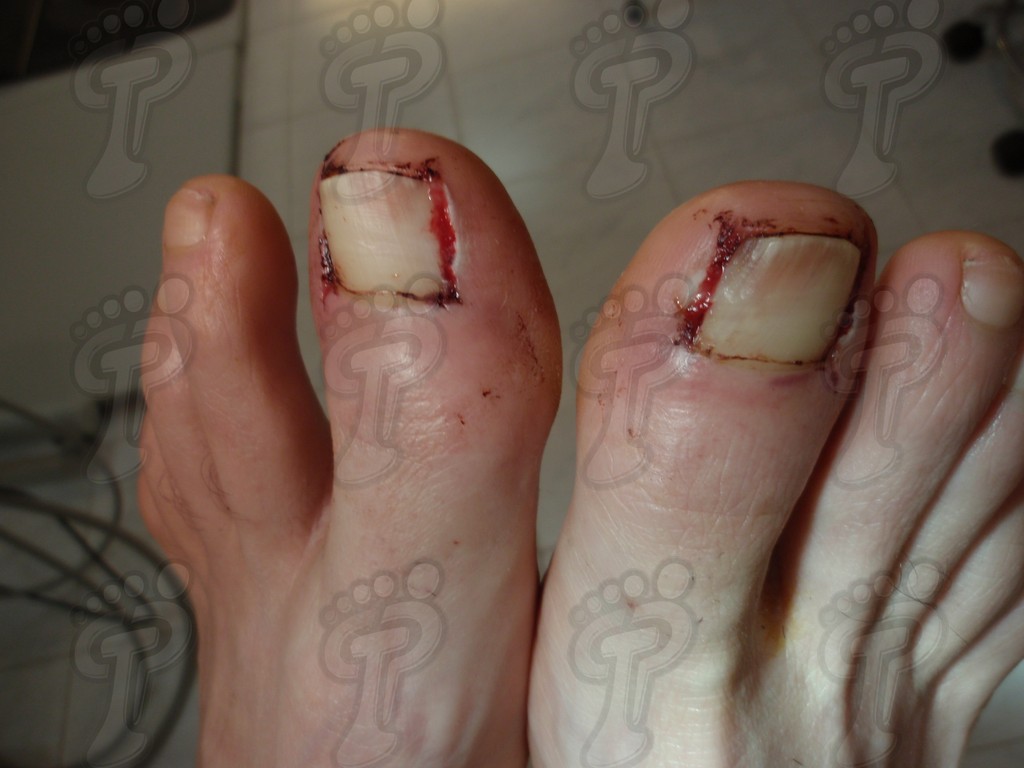
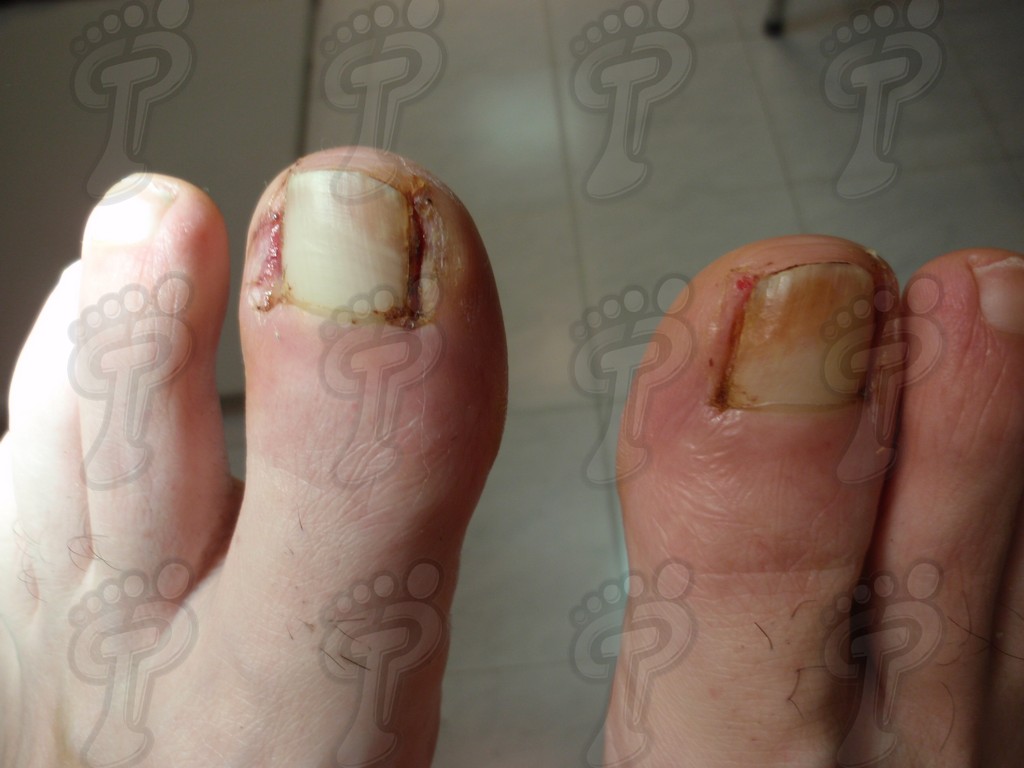
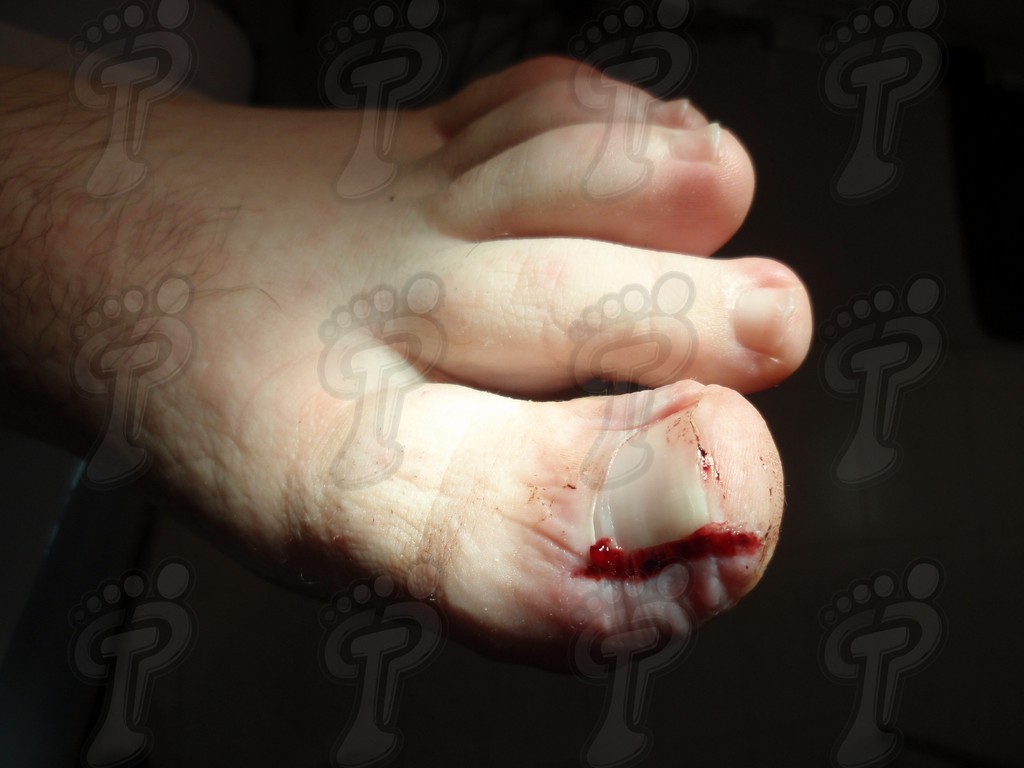
For those readers which are not familiarized with surgery, the cut form would be like an orange segment. When the excised tissue prevents a good coaptation from the surgical brims, we resort to the Winograd technique. This technique is similar to the esthetics regeneration, but from a distal point, it covers the eponychium to another of the hyponychium (5 milimeters in both cases). Once the technique is finished, we proceed to a surgical cleaning with physiologic serum and we joint together the surgical wound by approximation strips.






Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!