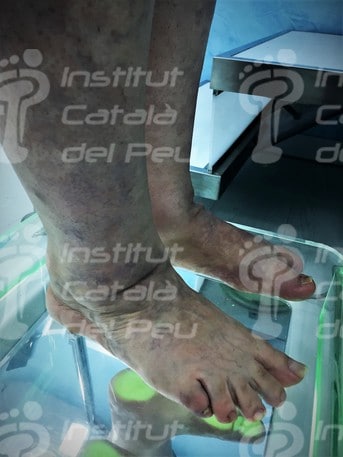
Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome is a congenital affectation of osseous development, blood vessels and soft tissues.
The main features of this syndrome are:
- The appearance of a red birthmark called a port-wine stains or hemangioma planum in birth. It appears approximately in 90% of cases and it is located in legs, buttocks and abdomen. These stains may affect the subcutaneous tissue, bones, muscles or organs like the spleen, the liver or the colon.
- Increase in osseous growth and soft tissues. It may appear at birth and it develops throughout infancy. It grows both in osseous length and thickness, mostly as result of to the growth of soft tissues.
- The appearance of varicose veins. They are congenital and they are not detected until the child starts walk. They are located under the knee or laterally. When it is located above the knee, it affects to superficial and deep venous systemsand even certain organs.
Other complications of the Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome are lymphatic malformations at an obstructive or lymphedema level, as well as facial asymmetry, changes in the size of the head, syndactyly, paresthesia, decalcification, thrombosis, ulcers, etc.
The excessive growth of bones and soft tissues appear in infancy and usually affects only one leg (although it can also affect the torso and the arms). The affected leg by this excessive growth may experience pain, problems with walking or a feeling of heaviness.
The Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome has an unknown cause although it has a relation with the mutation of the PIK3CA gene associated with excessive growth.
The diagnosis must be done through a computerized tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, echography and lymphoscintiegraphy. The differential diagnosis must include venous dysplasia, lymphedema and osseous tumours.
Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome is a progressive benign process whose treatment is symptomatic and conservative in 60% of the cases.
Surgery is usually recommended when there is a lymphedema, cellulitis and a chronic venous insufficiency. The epiphysiodesis is also a technique that decreases excessive bone growths.
Sclerotherapy is non-surgical treatments used to normalise the flow of blood in the affected veins.
Compression clothing is also used to complement other procedures to reduce the volume through the use of intermittent pneumatic devices (they inflate and deflate at fixed intervals).
Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome.
Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome. You can see the bigger size of the left foot.
Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome. You can see the appearance of Port-wine stains.
Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome. You can see the appearance of varicose veins.
Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome. You can see the thickness difference between both extremities.
Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome. You can see the difference of both front parts of feet.
Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome. You can see the asymmetry of the plantar footprint of the front part of the foot.