THE NEUROFIBROMATOSIS. CAUSES, DETECTION AND TREATMENT.
The neurofibromatosis is an alteration of the nervous system which affect directly in the growth and development of neural cells.
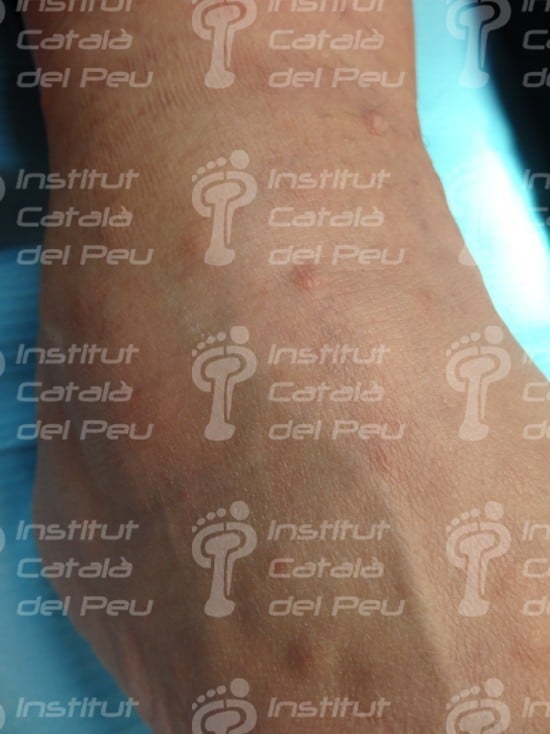
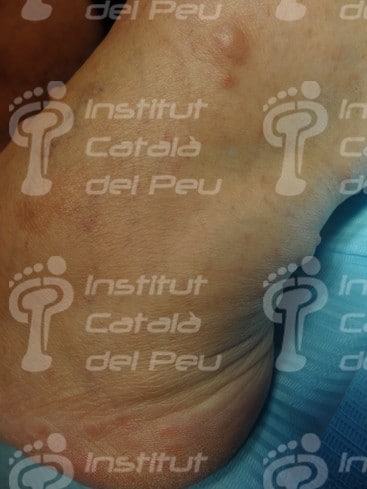
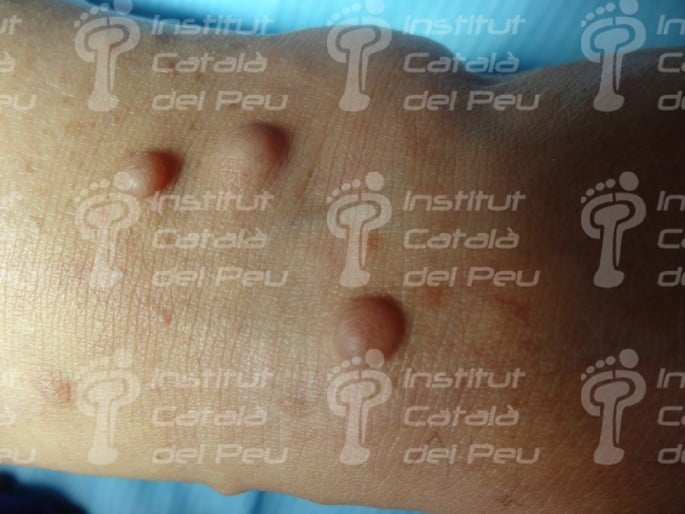
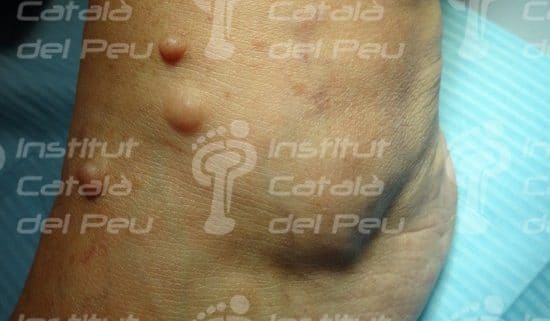
These alterations cause the development of tumors in nerves, as well as osseous deformities and changes in the skin. These tumors are not usually malignant, although they can cause serious aesthetic problems. They are genetically transmitted in an autosomal way, reaching 50 % of probabilities of passing on the disease from parents to children. They are classified in type 1 or type 2 depending on the alterated chromosome.
The type 1 neurofibromatosis or Recklinghausen’s disease is one of the most frequent genetic diseases and it shows a wide clinical manifestation.
In the past, the type 1 neurofibromatosis was known as peripheral neurofibromatosis because there were symptoms like tumors and cutaneous spots which were connected to the peripheral nervous system. Nowadays, it isn’t known with this name, because it is proved the existence of tumors in the central nervous system. Its main feature is the appearance of “café au lait spots”, long bones dysplasias, cataracts, etc.
The type 2 neurofibromatosis is characterized by the predominance of tumors in cranial nerves.
The cause of the neurofibromatosis is the mutation in the type 1 of the 17th chromosome, whereas in type 2 the mutation is in the 22nd chromosome.
50 % of neurofibromatosis are produced by a spontaneous mutation.
The type 1 neurofibromatosis is diagnosed when there are two or more than two of the following symptoms:
- Parents, brothers or sisters affected by the type 1 neurofibromatosis.
- Axillary or inguinal freckles.
- The existence of two or more than two neurofibromas.
- The existence of six or more than six “café au lait spots” bigger than 5 milimeters of diameter before puberty or bigger than 15 milimeters after puberty.
- Gliomas in optical tracts.
- The existence of a peculiar osseous lesion.
- The existence of two or more than two Lisch nodules.
The type 2 neurofibromatosis like the type 1 neurofibromatosis must consider two or more than two symptoms:
- Bilateral tumor of the eighth cranial pair.
- Parents, brothers or sisters, or children with type 2 neurofibromatosis and a unilateral acoustic tumor.
- Parents, brothers or sisters, or children with two of the following disorders.
a) Glioma.
b) Neurofibromatosis or Schwannoma.
c) Precocious cataract.
d) Meningioma.
The diagnoses are based on the ocular checkup, genetic tests and magnetic resonance of the brain or of the affected zone.
The most frequent complications of the type 1 neurofibromatosis are: scoliosis, macrocephaly, vertebral and cerebral tumors, costiveness, deafness, hypertension, etc.
In the type 2 neurofibromatosis, the complications generally take place on the functional of the nerve, like for instance, vision loss, chronic pain, facial paralysis, deafness, balance loss and feeling loss.
The treatment is palliative, treating the complication in different ways. In case of compression of organs by tumors we resort to surgery and in those cases of malignancy of tumors we resort to chemotherapy.
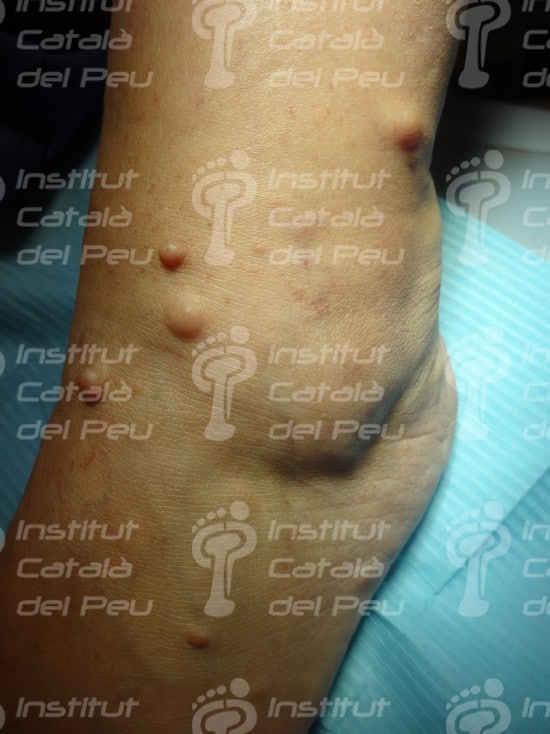
Neurofibromatosis
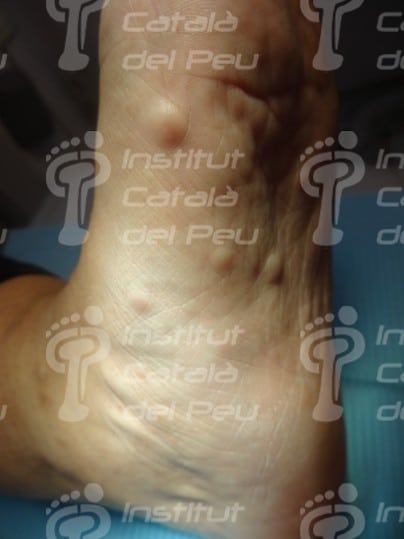
Neurofibromatosis
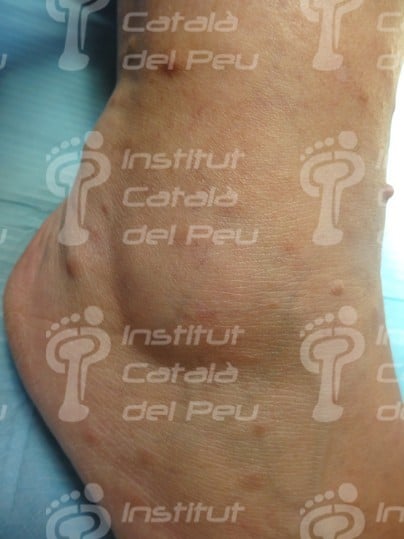
Neurofibromatosis
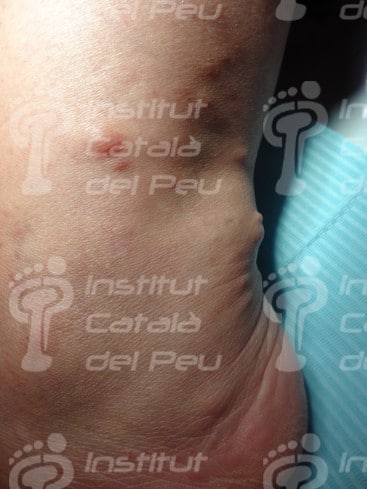
Neurofibromatosis

Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis







Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!